

When a program begins executing in the main() function, all variables declared within main() will be stored on the stack. Size = calcSize(10) /* dynamic heap storage */ Str = malloc(50) /* allocates 50 bytes of dynamic heap storage */ Before we start explaining, let's take a look at the following example: int x /* static stack storage */ No other function in the program can be called main().
For example every C, C++, or C# program must have one function named main(). When a program begins running, the system calls the function main() which marks the entry point of the program. Most object-oriented languages have some defined structure, and some come with so-called main() function. Heap and stack from programming perspective The stack is much faster than the heap but also smaller and more expensive. Heap is usually being used by a program for many different purposes. The pattern of allocation and size of blocks is not known until run time.

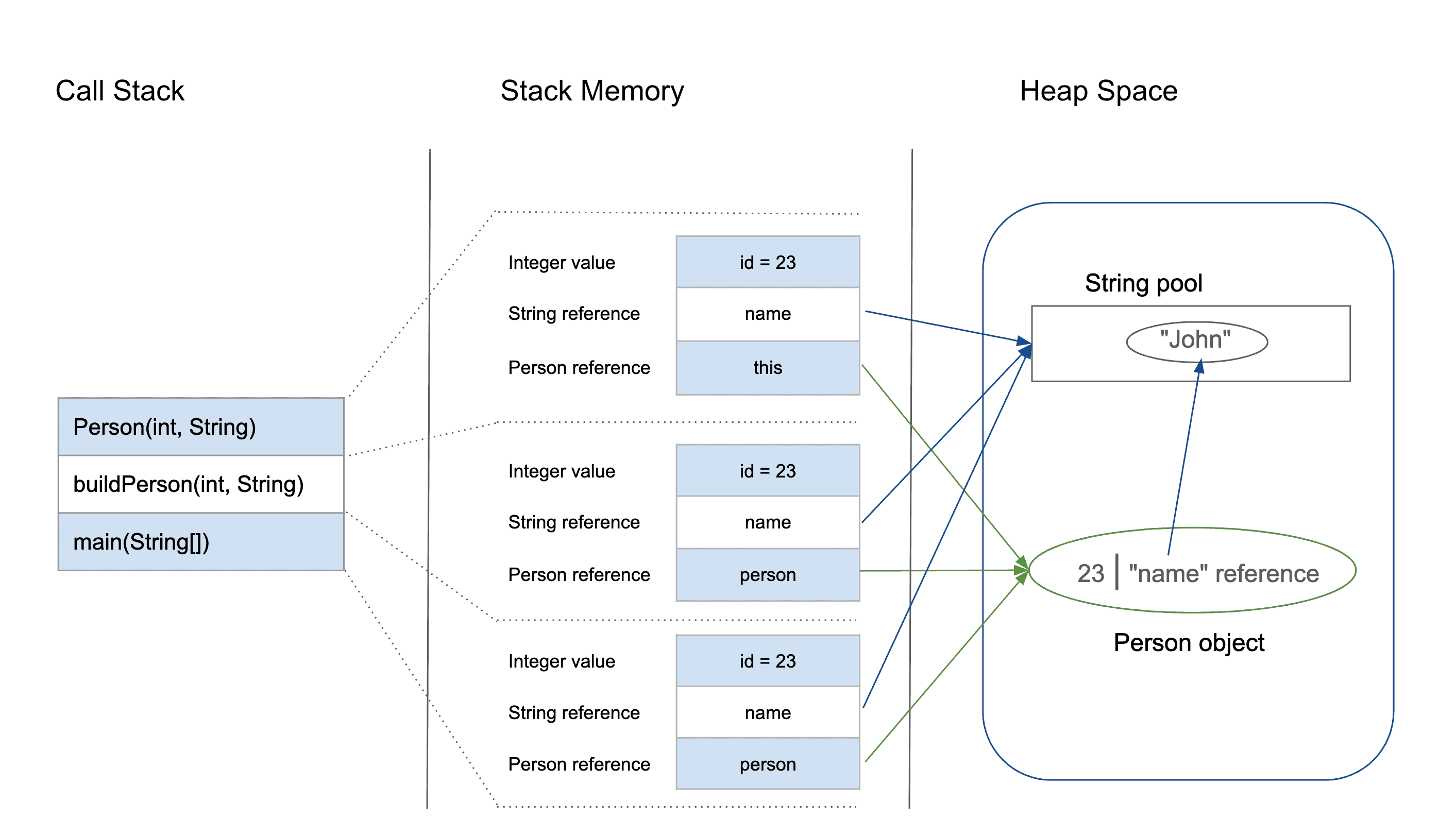
Blocks of memory are allocated and freed in this case in an arbitrary order. On the other hand, heap is an area of memory used for dynamic memory allocation. This means that storage in the memory is allocated and deallocated at only one end of the memory called the top of the stack. Stack is a section of memory and its associated registers that is used for temporary storage of information in which the most recently stored item is the first to be retrieved. The stack is the section of memory that is allocated for automatic variables within functions.ĭata is stored in stack using the Last In First Out (LIFO) method.
VARIABLE STORED JAVA STACK VS HEAP CODE
The two sections other from the code segment in the memory are used for data. This includes all user defined as well as system functions. It is the machine code, the computer representation of the program instructions. When you open some EXE file in Notepad, you can see that it includes a lot of "Gibberish" language, something that is not readable to human. The text segment (often called code segment) is where the compiled code of the program itself resides. When you look at your computer memory, it is organized into three segments: The distinction between stack and heap relates to programming.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
